Table of Contents
Introduction
If you or someone you know has multiple sclerosis (MS), you’ve probably heard of Mayzent (siponimod) – a breakthrough oral medication designed to slow the progression of the disease and reduce the number of relapses. But how does Mayzent work?
This guide breaks down how does Mayzent work in simple terms, exploring how it interacts with the immune system, protects nerve cells and supports the long-term management of MS. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver or healthcare professional, you’ll gain a clear understanding of what makes Mayzent unique in MS treatment.
What Is Mayzent?
Mayzent (siponimod) is an FDA-approved oral medication used to treat adults with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, including:
• Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS)
• Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS)
• Active Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS)
It was developed by Novartis Pharmaceuticals and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2019.
Unlike older injectable MS therapies, Mayzent offers the convenience of a once-daily tablet — but what really sets it apart is how it works at the immune-cell level.
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Before we explore how does Mayzent works, it’s important to understand what happens in multiple sclerosis.
In MS, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks myelin, the protective coating that surrounds nerve fibers in the central nervous system (CNS). This damage disrupts communication between the brain and the rest of the body, causing symptoms such as:
• Muscle weakness or stiffness
• Fatigue
• Balance and coordination problems
• Cognitive challenges
Over time, the loss of myelin can permanently damage nerves, resulting in progressive disability.
How Does Mayzent Work?
Now, let’s answer the central question — how does Mayzent work in multiple sclerosis?
Mayzent belongs to a class of drugs known as Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators. Its active ingredient, siponimod, selectively targets specific subtypes of S1P receptors on immune cells — primarily S1P1 and S1P5.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how does Mayzent works:
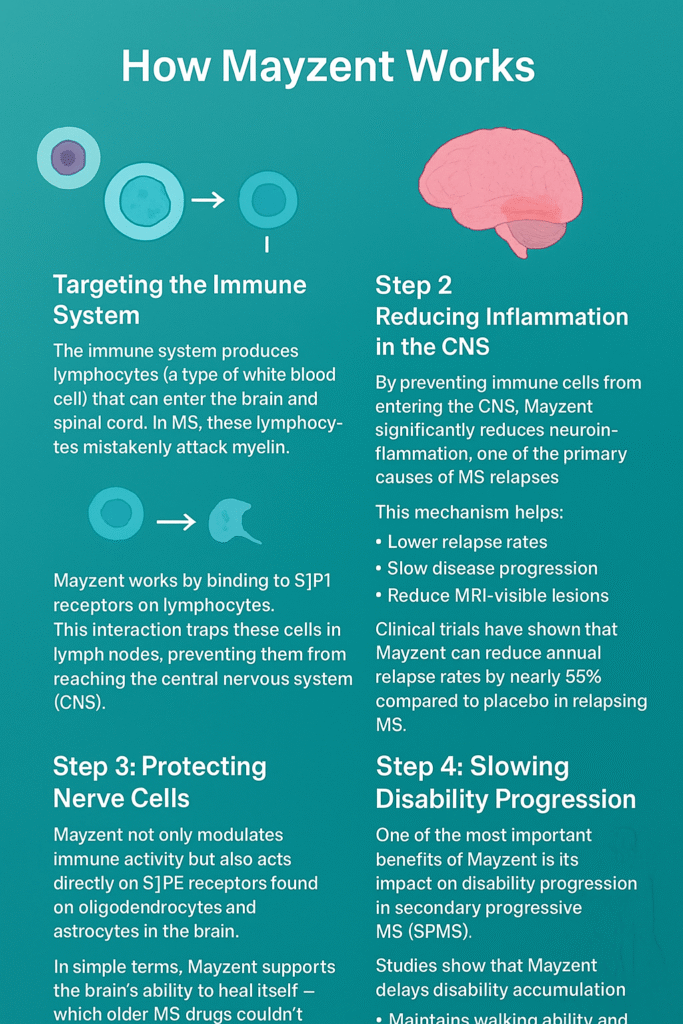
Step 1: Targeting the Immune System
The immune system produces lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that can enter the brain and spinal cord. In MS, these lymphocytes mistakenly attack myelin.
Mayzent works by binding to S1P1 receptors on lymphocytes. This interaction traps these cells in lymph nodes, preventing them from reaching the central nervous system (CNS).
Result:
Fewer immune cells attack the brain and spinal cord — reducing inflammation and myelin damage.
Step 2: Reducing Inflammation in the CNS
By preventing immune cells from entering the CNS, Mayzent significantly reduces neuroinflammation, one of the primary causes of MS relapses.
This mechanism helps:
- Lower relapse rates
- Slow disease progression
- Reduce MRI-visible lesions
Clinical trials have shown that Mayzent can reduce annual relapse rates by nearly 55% compared to placebo in relapsing MS.
Step 3: Protecting Nerve Cells
Mayzent not only modulates immune activity but also acts directly on S1P5 receptors found on oligodendrocytes and astrocytes in the brain.
This contributes to:
- Neuroprotection (protecting existing nerve cells)
- Remyelination support (helping repair damaged myelin)
- Improved brain volume preservation
In simple terms, Mayzent supports the brain’s ability to heal itself — something many older MS drugs couldn’t achieve.
Step 4: Slowing Disability Progression
One of the most important benefits of Mayzent is its impact on disability progression in secondary progressive MS (SPMS).
Studies show that Mayzent:
- Delays disability accumulation
- Maintains walking ability and motor function
- Slows cognitive decline
The EXPAND trial demonstrated a 21% reduction in the risk of disability progression in SPMS patients treated with Mayzent versus placebo.
Mayzent Dosing and Administration
Mayzent is taken orally once daily after an initial dose titration period.
Typical dosing schedule:
- Days 1–5: Gradual dose increase
- Day 6 onward: Maintenance dose (2 mg daily for most patients)
Because Mayzent can affect heart rate, genetic testing (CYP2C9 genotype) and first-dose monitoring may be required before starting treatment.
Pharmacokinetics: How Mayzent Moves in the Body
- Absorption: Reaches peak blood concentration in 4 hours.
- Half-life: Around 30 hours, meaning it stays active for more than a day.
- Metabolism: Primarily metabolized by the CYP2C9 enzyme in the liver.
- Elimination: Excreted via urine and feces.
Understanding this helps healthcare providers tailor dosing for patients with specific genetic variations or liver issues.
Who Can Take Mayzent?
Mayzent is approved for adults with:
- Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS)
- Active secondary progressive MS (SPMS)
- Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)
It is not typically used for primary progressive MS (PPMS) because studies have not shown significant benefit in that group.
Who Should Avoid Mayzent?
After knowing how does Mayzent work we can conclude ,Certain patients should not take Mayzent or should use it with caution, including those who:
- Have recent heart attack, stroke, or heart failure
- Have uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Are taking other immunosuppressants
- Have severe liver impairment
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding (Mayzent may cause fetal harm)
Always consult a neurologist before starting treatment.
Mayzent vs. Other MS Drugs
Understanding how does Mayzent work and comparing it with similar drugs like Mayzent vs Gilenya gives patients better clarity on treatment options.
| Feature | Mayzent (Siponimod) | Gilenya (Fingolimod) | Ocrevus (Ocrelizumab) |
| Type | S1P modulator | S1P modulator | Monoclonal antibody |
| Route | Oral (tablet) | Oral (tablet) | IV infusion |
| Key Action | Targets S1P1, S1P5 | Targets S1P1,3,4,5 | B-cell depletion |
| Use | RRMS, SPMS | RRMS | RRMS, PPMS |
| Heart monitoring | Yes (first dose) | Yes | Not required |
| Neuroprotection | Moderate | Low | High |
Takeaway:
Mayzent offers a balance of immune control, neuroprotection, and convenience, making it a strong option for long-term MS management.
Side Effects of Mayzent
Like any medication, Mayzent may cause side effects. Most are mild and manageable with medical supervision.
Common side effects include:
- Headache
- High blood pressure
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Swelling in hands or feet
- Abnormal liver function tests
Serious but rare side effects:
- Slow heart rate (especially after first dose)
- Vision problems due to macular edema
- Infections due to low white blood cell count
- Breathing difficulties
If any serious side effects occur, contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Drug Interactions
Mayzent may interact with:
- Beta-blockers (e.g., atenolol, metoprolol)
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., amiodarone)
- Immunosuppressants (e.g., methotrexate, cyclosporine)
- Strong CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole)
Always provide a full list of medications and supplements to your healthcare provider before starting Mayzent.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Mayzent
EXPAND Study (2018)
- Population: 1,651 patients with secondary progressive MS
- Results: 21% reduction in confirmed disability progression; 55% reduction in MRI lesion volume
BOLD Study
- Demonstrated Mayzent’s dose-dependent reduction in new active lesions in RRMS patients.
Long-Term Data
Ongoing follow-ups suggest that continuous use of Mayzent maintains brain volume and cognitive function over several years.
Lifestyle and Monitoring During Mayzent Therapy
To maximize Mayzent’s effectiveness:
- Follow a balanced anti-inflammatory diet
- Engage in regular physical therapy or exercise
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
- Get routine eye exams, liver tests, and blood counts
These steps help reduce side effect risks and support neurological health.
Key Takeaways — How Does Mayzent Work?
| Mechanism | Effect |
| Blocks lymphocyte movement | Reduces immune attack on CNS |
| Decreases CNS inflammation | Fewer relapses |
| Activates neuroprotective receptors | Preserves brain tissue |
| Slows progression | Delays disability |
| Oral administration | Convenient for patients |
In short, how does Mayzent work ?
Mayzent works by modulating immune cell activity and protecting the brain from inflammatory damage, helping MS patients maintain better long-term function.
Conclusion
So, how does Mayzent work?
Mayzent (siponimod) is a next-generation MS therapy that prevents harmful immune cells from entering the brain and spinal cord, while at the same time protecting nerve cells from damage.
By targeting specific S1P receptors, it offers dual benefits – immunomodulation and neuroprotection – which makes it a valuable treatment option for relapsing and secondary progressive MS.