Table of Contents
Introduction
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to Zongertinib (brand name Hernexeos) on August 8, 2025, marking a significant milestone in lung cancer treatment. Zongertinib is approved for adults with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors harbor HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) activating mutations and who have received prior systemic therapy. This decision is based on promising data from the Phase 1b BEAMION LUNG-1 study.
In this blog, we will provide a detailed overview of Zongertinib FDA approval, its mechanism of action, clinical trial results, benefits, risks, and its future impact on the treatment landscape of HER2-mutated NSCLC.
What is Zongertinib?
Zongertinib (Hernexeos) is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) specifically designed to target HER2 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. HER2, also known as ERBB2, is a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family that plays a vital role in regulating cell growth and survival. Mutations in the HER2 tyrosine kinase domain are associated with uncontrolled tumor growth and poor prognosis in NSCLC.
Unlike existing HER2-directed therapies primarily used in breast or gastric cancers, Zongertinib directly addresses HER2-mutant lung cancer, a subset that previously had limited targeted treatment options.
Zongertinib FDA Approval
The accelerated Zongertinib FDA Approval was based on compelling evidence from the BEAMION LUNG-1 study, which demonstrated clinically meaningful responses in patients with HER2-mutated NSCLC who had progressed on prior systemic therapies.
This accelerated approval pathway allows earlier access to potentially life-saving treatments for patients with serious or life-threatening conditions. However, further confirmatory trials will be required to establish long-term survival benefits and potentially secure full approval.
Key Highlights of the FDA Approval: –
Date: August 8, 2025
Indication: Adults with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) TKD mutations
Setting: Patients who have received prior systemic therapy
Approval type: Accelerated approval based on Phase 1b BEAMION LUNG-1 study
The BEAMION LUNG-1 Clinical Trial
The BEAMION LUNG-1 trial was a multicenter, open-label, Phase 1b study evaluating the safety and efficacy of Zongertinib in patients with advanced HER2-mutated NSCLC.
Key Findings from the BEAMION LUNG-1 Study: – Objective Response Rate (ORR): Zongertinib showed promising response rates in heavily pretreated patients. – Duration of Response (DoR): Many patients experienced durable responses lasting several months. – Progression-Free Survival (PFS): Median PFS indicated meaningful disease control compared to historical outcomes in this patient population. – Safety Profile: Zongertinib demonstrated a manageable safety profile with mostly mild-to-moderate adverse events.
This data strongly supported the FDA’s decision to grant accelerated approval.
Mechanism of Action of Zongertinib
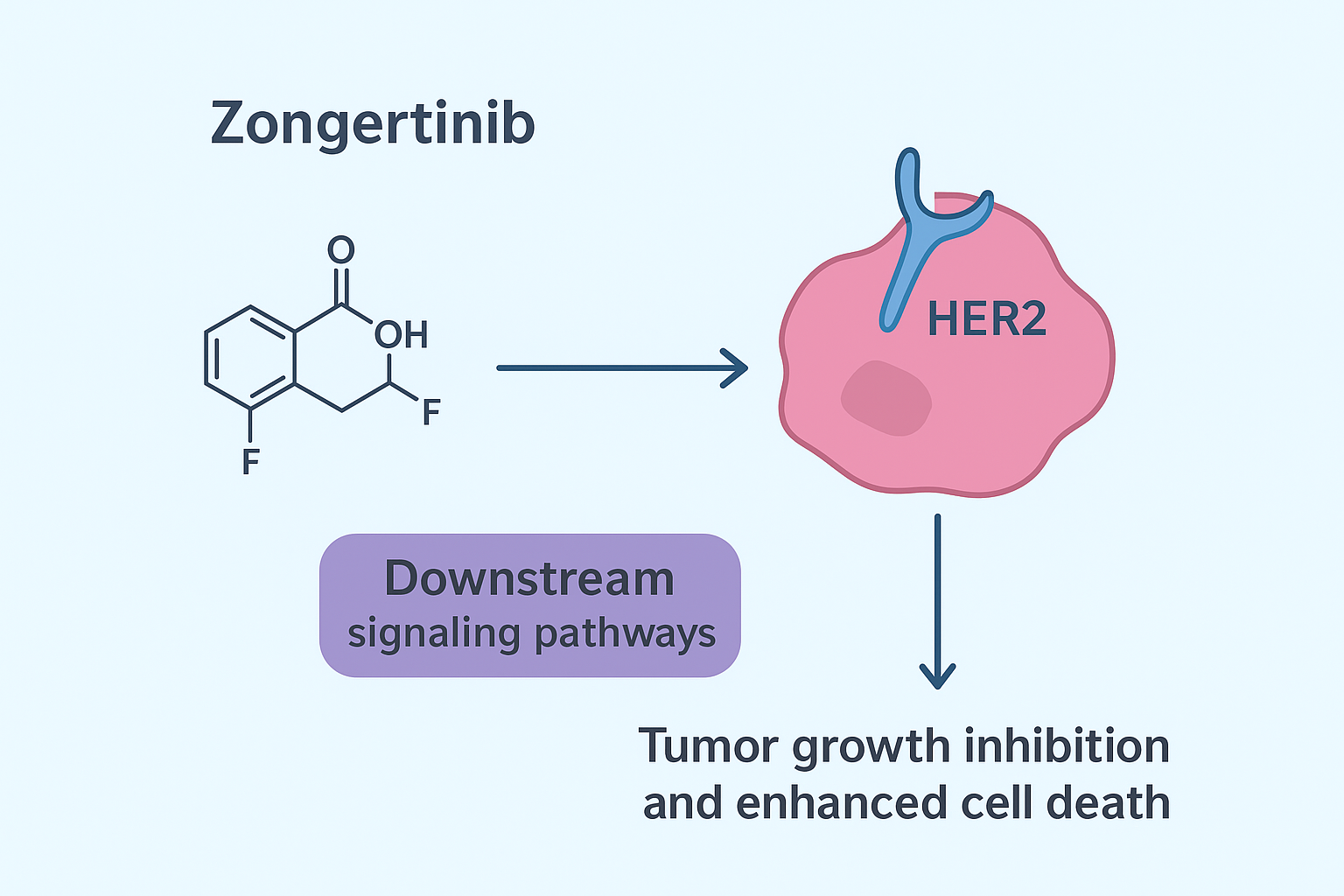
Zongertinib functions by irreversibly binding to the HER2 tyrosine kinase domain, thereby inhibiting the downstream signaling pathways responsible for uncontrolled cancer cell proliferation. This mechanism specifically targets tumors with HER2 TKD mutations, making it a precision medicine option for patients with this genetic alteration.
By blocking HER2-driven pathways, Zongertinib suppresses tumor growth and enhances cell death, offering a much-needed therapy for patients with limited alternatives.
Why is Zongertinib FDA Approval Important?
The Zongertinib FDA Approval is a landmark event for several reasons:
- First HER2-TKD targeted therapy in NSCLC: Until now, treatment options for HER2-mutated NSCLC were limited to chemotherapy and non-specific TKIs, which offered modest efficacy.
- Precision oncology advancement: Zongertinib exemplifies how targeted therapies can provide better outcomes by focusing on specific genetic alterations.
- Unmet medical need: HER2 mutations occur in approximately 2–4% of NSCLC patients, representing a population with few targeted options.
- Potential survival benefit: Although long-term data is pending, early trial results suggest improved disease control and quality of life.
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Like most cancer therapies, Zongertinib is associated with potential side effects. The most common adverse reactions observed in clinical studies include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Decreased appetite
- Skin rash
- Hepatotoxicity (elevated liver enzymes)
Most side effects were manageable with supportive care or dose modifications. Rare but severe toxicities require close monitoring
Comparing Zongertinib with Existing HER2 Therapies
Currently, trastuzumab-based regimens are widely used in breast and gastric cancers with HER2 overexpression, but their role in lung cancer remains limited. Other TKIs like poziotinib and pyrotinib have shown activity against HER2 mutations but with higher toxicity profiles.
Advantages of Zongertinib: – More selective inhibition of HER2 mutations – Favorable safety profile compared to earlier TKIs – Oral administration offering patient convenience – Demonstrated durable clinical responses
Future Directions and Ongoing Research
The acceleratedZongertinib FDA Approval paves the way for ongoing and future studies to further evaluate its benefits.
Ongoing Research Areas: – Confirmatory Phase 3 trials to validate clinical benefit – Combination studies with immunotherapies and chemotherapy – Research into resistance mechanisms and next-generation HER2 inhibitors – Expansion of use in earlier treatment lines or other HER2-driven cancers.
Patient Perspective
For patients with HER2-mutant NSCLC, the approval of Zongertinib represents hope and improved treatment possibilities. Previously, these patients had limited targeted options and often faced poor prognoses with standard chemotherapy. With Zongertinib, there is now an effective therapy that directly addresses their cancer’s genetic driver.
Zongertinib in the Global Market
While Zongertinib FDA Approval marks a crucial step in the United States, other regulatory authorities worldwide, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Health Canada, are expected to review Zongertinib. The global oncology community is closely monitoring these developments to ensure broader access.
Conclusion
The Zongertinib FDA Approval (Hernexeos) on August 8, 2025, marks a groundbreaking advancement in the treatment of HER2-mutated non-squamous NSCLC. Based on promising results from the BEAMION LUNG-1 study, Zongertinib offers a targeted, effective, and well-tolerated therapy for patients with limited options.
While further research is needed to confirm long-term survival benefits, this approval represents a major step forward in precision oncology. For patients and oncologists, Zongertinib provides renewed hope and a pathway toward better outcomes in the fight against lung cancer.