Table of Contents
Introduction
On February 14, 2025, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved vimseltinib, marketed under the brand name Romvimza™, for the treatment of tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) in adult patients. This is a significant advance for patients struggling with this rare, debilitating joint condition. Known as a switch-control kinase inhibitor of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), vimseltinib is the first oral therapy approved specifically for TGCT, offering hope to patients with previously limited treatment options.
In this comprehensive blog, we will explore the mechanism of action, FDA approval pathway, clinical trial data, benefits, side effects, patient outcomes, and the future outlook for vimseltinib FDA approval.
What is Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor (TGCT)?
Before diving into vimseltinib FDA approval, it is important to understand TGCT:
- TGCT Definition: TGCT is a rare, locally aggressive tumor that affects the synovium (the lining of joints and tendons).
- Symptoms: Patients often experience joint pain, swelling, stiffness, reduced mobility, and significant discomfort.
- Prevalence: TGCT is rare, occurring in approximately 11 cases per million people annually, making it an orphan disease.
- Current Challenges: Surgery has been the primary treatment. However, recurrence rates are high, and in many cases, the tumor is inoperable or resistant to surgery.
This is where vimseltinib FDA approval becomes a game-changer.
What is Vimseltinib (Romvimza™)?
- Drug Class: Vimseltinib is a switch-control kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R (colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor).
- Brand Name: Romvimza™
- Approval Date: February 14, 2025
- Indication: Treatment of adult patients with symptomatic TGCT not amenable to improvement with surgery.
- Dosage Form: Oral tablet, once-daily administration.
Vimseltinib FDA Approval: Key Highlights
The FDA approval of vimseltinib was based on strong clinical trial results that demonstrated its ability to significantly improve patient outcomes.
1. Regulatory Pathway
- Fast Track Designation: Granted to accelerate development.
- Orphan Drug Designation: Given due to the rarity of TGCT.
- Priority Review: To bring therapy to patients faster.
2. Pivotal Clinical Trial: MOTION Study
The approval was primarily supported by data from the Phase 3 MOTION trial, which compared vimseltinib with placebo.
- Participants: Adult patients with advanced TGCT.
- Primary Endpoint: Overall response rate (ORR) measured by RECIST criteria.
- Results:
- ORR significantly higher in the vimseltinib arm.
- Patients reported less pain, improved joint mobility, and reduced stiffness.
- Safety Profile: Side effects were generally manageable and consistent with CSF1R inhibition.
3. Significance of Approval
The vimseltinib FDA approval represents the first oral targeted therapy specifically approved for TGCT, offering patients a non-surgical, effective treatment option.
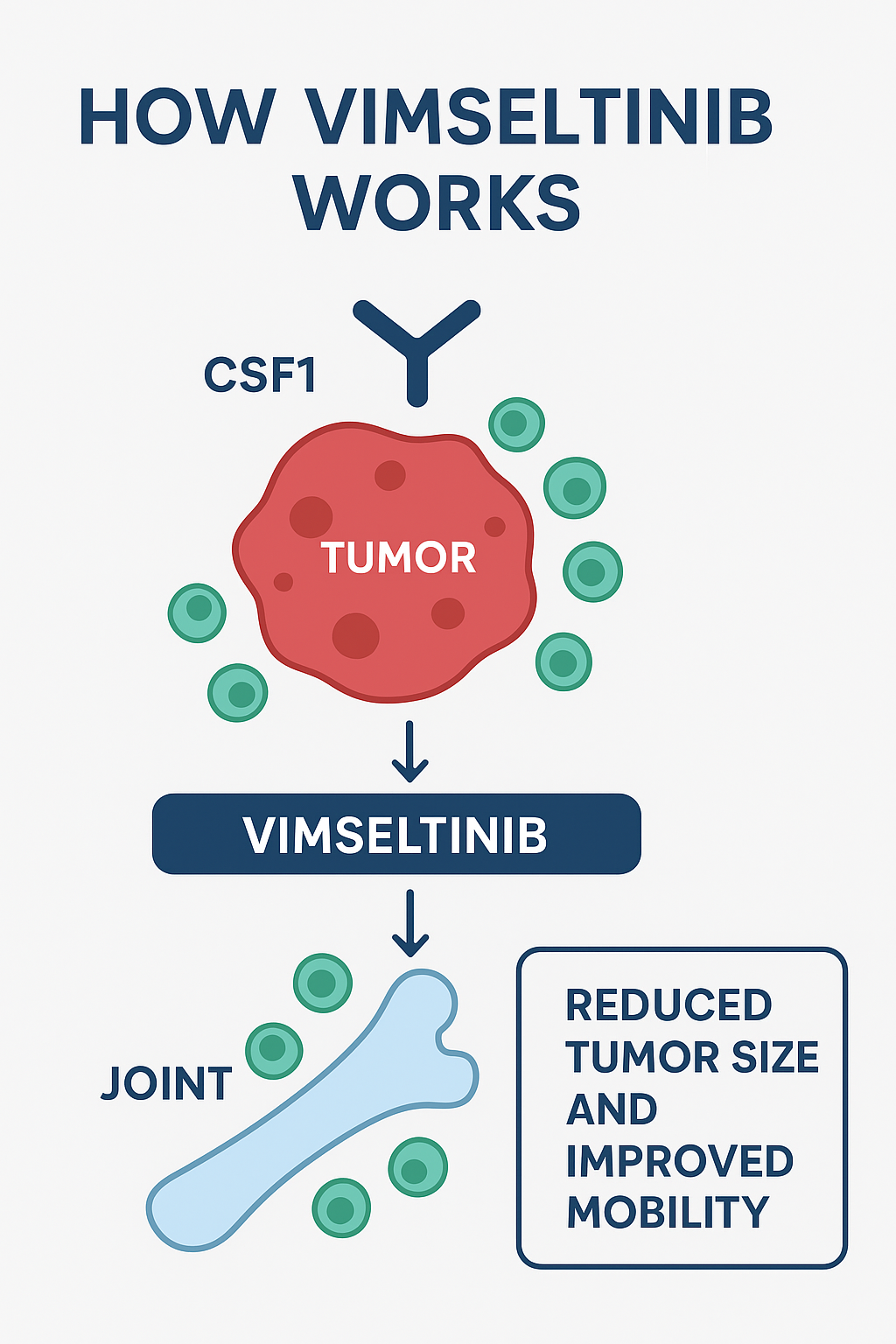
Mechanism of Action: How Vimseltinib Works
Vimseltinib acts as a switch-control kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R, which is involved in macrophage proliferation and survival.
• CSF1R in TGCT: TGCT tumors are driven by overproduction of CSF1, which leads to macrophage recruitment and tumor growth.
• Role of vimseltinib: By selectively inhibiting CSF1R, vimseltinib reduces macrophage activity and tumor growth, reducing symptoms.
• Outcomes: Improved joint function, tumor size reduction, and improved quality of life.
This precision medicine approach highlights the importance of targeted cancer-like therapies in non-malignant tumor conditions.
Clinical Benefits of Vimseltinib
Patients treated under the vimseltinib FDA approval program reported multiple benefits:
- Reduction in Tumor Size – Significant shrinkage of TGCT lesions.
- Improved Mobility – Patients experienced less stiffness and regained movement.
- Pain Relief – Many reported a decrease in joint pain.
- Non-Surgical Option – Critical for patients not eligible for surgery.
- Oral Administration – Convenient daily pill, no hospital-based infusions.
Safety Profile and Side Effects
While vimseltinib FDA approval is promising, patients should be aware of potential side effects.
Common Side Effects:
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Increased liver enzymes (ALT/AST elevation)
- Diarrhea
- Rash
- Headache
Serious Side Effects:
- Liver toxicity (requires monitoring)
- Low white blood cell counts
- Rare allergic reactions
Monitoring Guidelines:
- Regular liver function tests
- Complete blood counts (CBC)
- Clinical assessment of symptoms
Overall, the safety profile was favorable compared to other available therapies.
Comparison with Other TGCT Therapies
Before vimseltinib FDA approval, TGCT management options were limited:
- Surgery – Primary treatment, but recurrence rates up to 50%.
- Pexidartinib (Turalio®) – The first systemic therapy (2019), also a CSF1R inhibitor, but associated with severe liver toxicity and requires REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy).
Why Vimseltinib Stands Out:
- Oral daily dosing
- Lower incidence of severe hepatotoxicity
- Improved tolerability profile
- Demonstrated mobility improvements
Thus, vimseltinib FDA approval offers a safer, more accessible treatment compared to existing options.
Patient Perspective: A New Era in TGCT Treatment
For TGCT patients, the FDA approval of vimseltinib is not just a medical milestone – it is a life-changing advancement.
• Patients with inoperable tumors now have real hope.
• Daily functioning and quality of life are significantly improved.
• Reduced pain allows patients to return to work, hobbies, and normal activities.
Patient advocacy groups have hailed the approval as a revolutionary step forward in the treatment of rare diseases.
Economic and Market Impact
The vimseltinib FDA approval also has implications for the pharmaceutical market:
- Orphan Drug Status ensures market exclusivity for 7 years.
- Pricing strategies are expected to align with other rare disease therapies.
- Healthcare providers may see increased adoption due to oral convenience and favorable safety.
Industry analysts predict Romvimza™ could generate strong market demand in the TGCT community.
Future Research and Expansions
Although the FDA approval of vimseltinib is currently limited to TGCT, ongoing research explores its potential in other CSF1R-driven conditions.
- Possible applications in oncology, inflammatory diseases, and macrophage-driven disorders.
- Combination studies with immunotherapies are under consideration.
This opens the door for broader therapeutic use in the future.
Conclusion
The FDA approval of vimseltinib is a historic milestone for patients with tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT). With the launch of Romvimza™, patients finally have access to a safe, effective, and convenient oral therapy that improves symptoms, increases mobility, and reduces the need for surgery.
As research continues, vimseltinib may also find a role in other macrophage-driven conditions, making this approval not only a breakthrough for TGCT but also a gateway to future treatments.
For now, patients and healthcare providers can rejoice in the fact that the FDA approval of vimseltinib has revolutionized the treatment of this rare and debilitating condition.

