Table of Contents
Introduction
The field of biotechnology is constantly evolving, bringing new treatment options to conditions that were once considered difficult to manage. Among these innovations, clesrovimab-cfor, marketed under the brand name Enflonsia, has emerged as a promising monoclonal antibody therapy. Designed with advanced biotechnology, clesrovimab is gaining attention in the clinical practice and research communities for its targeted therapeutic effects.
In this blog post, we will provide a comprehensive overview of clesrovimab, including its background, mechanism of action, approved indications, dosage guidelines, benefits, potential risks, market availability, cost factors, and frequently asked questions. Whether you are a healthcare professional, patient, or researcher, this article will help you understand why clesrovimab (Enflonsia) is making headlines in 2025.
What is Clesrovimab (Enflonsia)?
Clesrovimab-cfor is a monoclonal antibody developed to specifically target immune pathways associated with inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. The drug is marketed under the brand name Enflonsia. Unlike traditional small-molecule drugs, clesrovimab works by binding to specific proteins in the body, thereby modulating immune responses with high precision.
Monoclonal antibodies like clesrovimab are laboratory-engineered proteins that mimic the immune system’s natural defense mechanisms. By binding to disease-related targets, they can alter disease progression, reduce inflammation, or improve immune regulation.
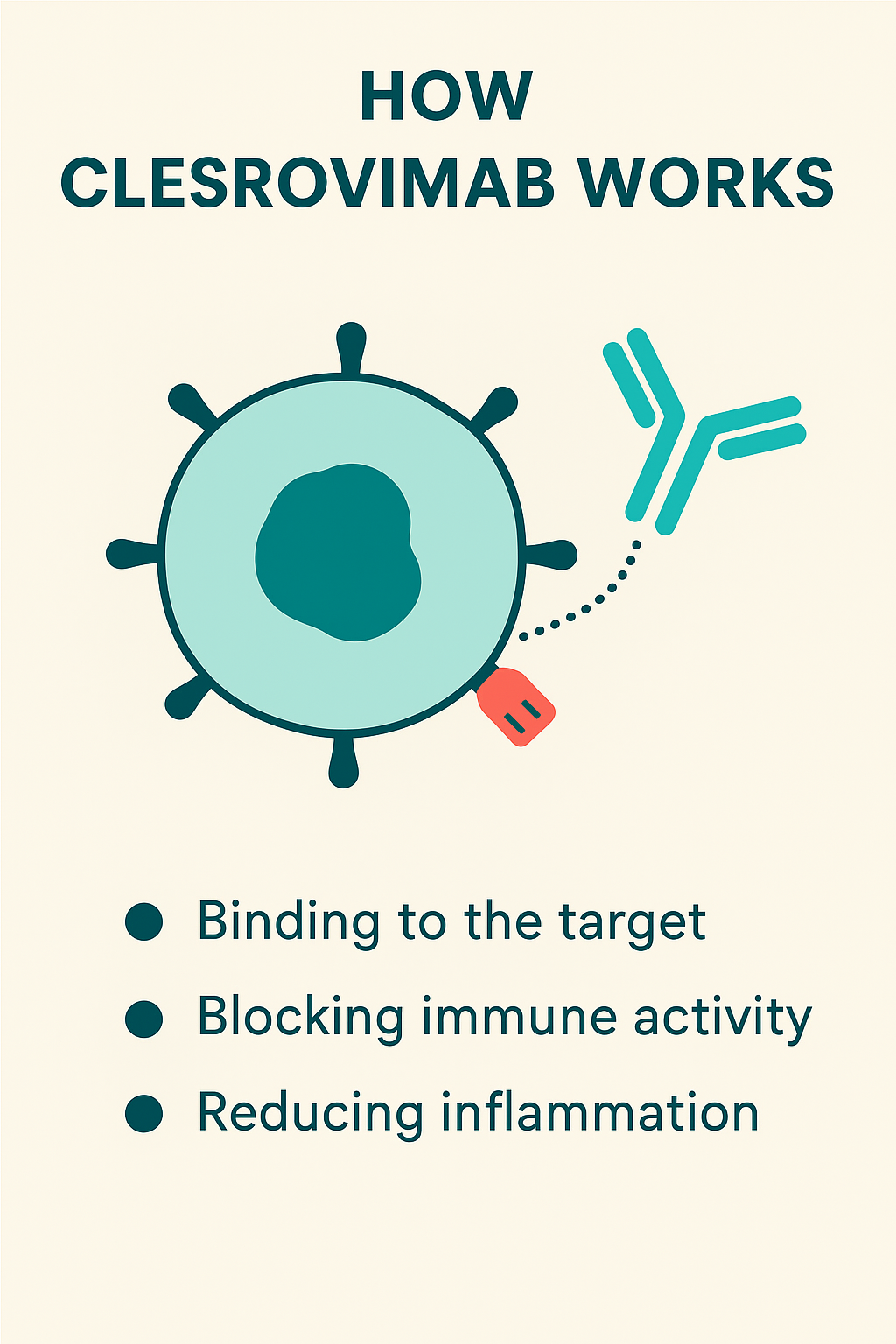
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action (MOA) of Enflonsia is based on target-specific immune modulation. It binds to a specific receptor on immune cells, thereby preventing the abnormal activation of inflammatory pathways.
• Binding specificity – clesrovimab selectively binds to its receptor, thereby reducing unwanted immune activity.
• Immune modulation – By inhibiting overactivity, it helps restore immune balance.
• Anti-inflammatory effects – clesrovimab reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine release, improving symptoms of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
• Tissue protection – Long-term administration may reduce tissue damage caused by chronic inflammation.
This highly targeted action makes clesrovimab (Enflonsia) a valuable treatment option for diseases where conventional treatments have had limited success.
Approved Indications of Enflonsia
As of 2025, clesrovimab has been approved in certain regions to treat the following:
1. Autoimmune disorders – specifically conditions with excessive immune activity.
2. Chronic inflammatory diseases – such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
3. Immune-mediated respiratory conditions – Ongoing trials suggest potential use in asthma and pulmonary fibrosis.
4. Rare genetic disorders – Some clinical studies are investigating its benefits in orphan diseases, including immune disorders.
Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are continually reviewing new data to expand its label to more conditions.
Clinical Trial Evidence Supporting Enflonsia
Clinical trials are central to understanding the safety and efficacy of clasrovimab.
• Phase 1 trials: demonstrated safety, tolerability, and predictable pharmacokinetics.
• Phase 2 trials: demonstrated significant reductions in disease activity scores in patients with autoimmune disorders.
• Phase 3 trials: currently underway, confirming its efficacy compared to standard treatments.
Real-world evidence: Early post-approval studies show strong patient adherence and good outcomes.
Results suggest that clasrovimab (Enflonsia) could be a next-generation therapy in immune-mediated diseases.
Dosage and Administration of Clesrovimab
The dosage of clasrovimab varies depending on the indication, patient weight, and medical condition.
• Route of administration: Intravenous (IV) infusion or subcutaneous injection.
• Initial dose: Usually a loading dose to quickly achieve therapeutic levels.
• Maintenance dose: Given at regular intervals (every 2-4 weeks).
• Duration of treatment: Long-term use may be required for chronic diseases.
Patients receiving clasrovimab should be monitored for infusion-related reactions, liver function, and immune status.
Benefits of Enflonsia
1. Targeted therapy – High specificity reduces systemic side effects.
2. Improved disease control – Effective for conditions that are resistant to conventional treatments.
3. Improved quality of life – Patients see significant improvement in symptoms.
4. Reduced hospitalizations – Helps reduce disease progression and hospitalizations.
5. Ongoing research – Potential new indications in oncology and rare diseases.
Side Effects and Safety Profile of Enflonsia
Like all biologics, clesrovimab has potential side effects.
Common Side Effects:
- Injection site reactions
- Fatigue and mild headache
- Nausea
- Mild upper respiratory infections
Serious Side Effects:
- Infusion-related reactions (fever, chills, rash)
- Increased risk of infections
- Possible liver enzyme elevations
- Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions
Healthcare providers recommend close monitoring during and after treatment.
Clesrovimab vs Other Monoclonal Antibodies
Compared to existing biologics, clasrovimab offers several advantages:
• High binding specificity → fewer off-target effects
• Less frequent dosing → improved patient compliance
• Promising trial results → effective in resistant patient populations
This positions clasrovimab (Enflonsia) as a strong competitor in the monoclonal antibody market.
Cost and Market Availability
The biggest factor to consider when considering biologic drugs is cost.
• Estimated price range: $3,000–$6,000 per month, depending on indication and healthcare setting.
• Insurance coverage: Many insurance companies offer partial reimbursement for biologics such as clesrovimab.
• Patient assistance programs: Manufacturers often offer financial assistance programs.
• Global availability: Currently approved in select regions, regulatory submissions are ongoing in other markets.
Future Prospects of Clesrovimab
Researchers are exploring the role of Enflonsia beyond autoimmune diseases, including:
• Oncology: Investigating its potential in targeted cancer therapy.
• Neurological disorders: Trials are underway in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica.
• Pediatric use: Assessing safety in children with rare immune-mediated diseases.
With ongoing research, clasrovimab is expected to become a cornerstone therapy in precision medicine.
Patient Experience and Real-world Use
Patients taking Enflonsia often report:
• Significant relief of symptoms within a few weeks
• Reduced dependence on corticosteroids
• Reduced incidence of disease exacerbations
• Improved daily functioning and mobility
However, patient experiences vary and close guidance from a physician is required.
Conclusion
Clasrovimab-cfor (Enflonsia) represents a significant advance in monoclonal antibody therapy. Due to its targeted mechanism of action, favorable clinical outcomes, and potential to treat a wide range of diseases, clasrovimab is positioned as a transformative option in modern medicine.
While cost and availability remain challenges, continued research and widespread approval may help establish clasrovimab as a leading therapy in autoimmune, inflammatory, and potentially oncological conditions.

