Brand Name : Vanrafia
Generic Name : atrasentan
Drug Class : endothelial antagonist
Dosage Form : Oral tablets .
Table of Contents
Introduction :
Having too much protein in your urine isn’t just a symptom—it’s a red flag that indicates kidney damage. If left unchecked, proteinuria can lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and even end-stage renal failure. In 2025, a new treatment called Vanrafia was approved, bringing new hope to patients struggling with proteinuria, especially those who don’t respond well to standard treatments.
In this article, we’ll explore Vanrafia, a new therapeutic agent specifically designed to manage proteinuria. With its innovative mechanism of action and strong clinical support, Vanrafia is now considered a breakthrough in nephrology.
What is Vanrafia?
Vanrafia is a first-in-class, oral drug approved to reduce proteinuria in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly in patients with diabetic nephropathy, FSGS (focal segmental glomerulosclerosis) or IgA nephropathy.
It belongs to a new class of drugs that selectively target kidney-specific pathways, reducing inflammation and fibrosis, and restoring glomerular filtration function.
Vanrafia is marketed in the US and Europe by a leading biopharmaceutical company and received FDA approval in April 2025 following successful Phase III trials.
What is Proteinuria ?
Proteinuria occurs when the glomeruli, the filtering units of the kidney, become damaged, allowing proteins like albumin to pass into the urine.
Causes of Proteinuria:
- Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy)
- Hypertension
- Glomerulonephritis (IgA nephropathy, FSGS)
- Autoimmune diseases like Lupus
- Certain medications or infections
Persistent proteinuria is both a marker and a driver of kidney damage. Hence, controlling it is crucial to slow CKD progression.
Vanrafia Drug Class :
It is part of a new pharmacological class known as:
✳️ Selective Endothelin A Receptor Antagonists (sETArA)
It targets the endothelin pathway, which plays a central role in:
- Renal inflammation
- Podocyte injury
- Glomerular permeability
By selectively blocking endothelin A receptors, Vanrafia reduces glomerular pressure and protein leakage, preserving kidney function.
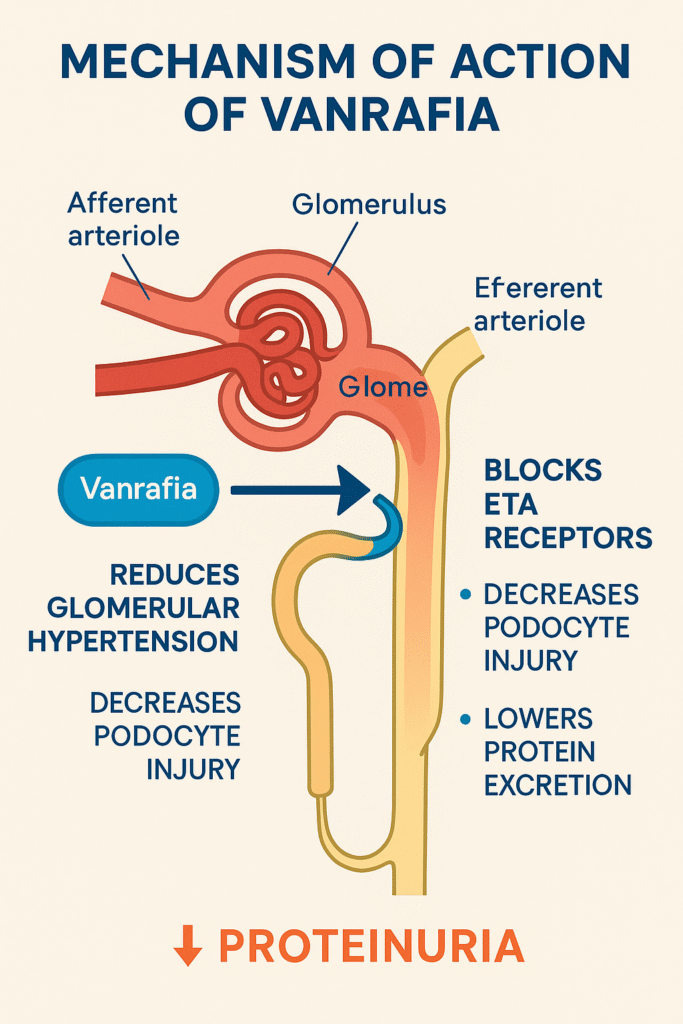
Mechanism of Action (MOA) :
It is works through the selective blockade of endothelin A (ETA) receptors, which are overactivated in patients with proteinuric kidney diseases.
Step-by-step MOA:
- Blocks ETA receptors on podocytes and vascular smooth muscles
- Reduces glomerular hypertension
- Decreases podocyte injury and detachment
- Lowers protein excretion in urine
- Slows CKD progression
Importantly, it spares endothelin B (ETB) receptors, which help maintain natriuresis and vasodilation—making it safer than non-selective endothelin blockers.
Indications and Uses :
As of 2025, Vanrafia is FDA-approved and EMA-authorized for –
| Indication | Approval Status |
|---|---|
| Proteinuria in Diabetic Kidney Disease | ✅ Approved |
| IgA Nephropathy | ✅ Approved |
| FSGS (Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis) | ✅ Approved |
| Lupus Nephritis | Under Investigation |
| Hypertensive Nephropathy | Off-label use |
It is prescribed when traditional therapies like RAAS blockers (ACE inhibitors or ARBs) are insufficient.
Clinical Trials & Efficacy :
🔬 VERA Trial (Phase III) –
- Study Population: 1,200 patients with diabetic nephropathy and persistent proteinuria
- Treatment Duration: 52 weeks
- Result:
- 42% reduction in urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR)
- Slower decline in eGFR
- Improved renal composite outcomes
🔬 VISION Trial (IgA Nephropathy) –
- Achieved a 35% reduction in proteinuria
- Slowed progression to dialysis or transplant by 18 months on average
These trials were instrumental in fast-tracking Vanrafia’s approval.
Dosage and Administration :
- Form: Oral tablets (available in 0.75 mg)
- Usual adult dose: 0.75 once daily
- With or without food
Dose adjustments:
- Required in hepatic impairment
- Not recommended in pregnancy or breastfeeding
Important: Patients should remain on stable doses of RAAS blockade unless contraindicated.
Storage Conditions :
To maintain the stability and effectiveness of tablet, follow these recommended storage guidelines:
- Store at room temperature:
20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F)
[Permitted excursions between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F)] - Protect from moisture and light:
Keep the tablets in the original blister pack or tightly closed container until use. - Do not refrigerate or freeze.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Do not use after the expiration date printed on the label or packaging.
Side Effects :
Tablets is well tolerated, but like any drug, it may cause side effects.
Common Side Effects:
- Nasal congestion
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Mild hypotension
- Fever
Rare but Serious:
- Fluid retention or edema
- Anemia
- Liver enzyme elevations
- Heart failure exacerbation
Monitoring:
Liver function tests and hemoglobin should be checked every 1–3 months.
Advantages of Vanrafia Over Traditional Therapies :
| Parameter | Vanrafia | ACE Inhibitors / ARBs |
|---|---|---|
| Target Pathway | Endothelin A | RAAS |
| Proteinuria Reduction | High (40–50%) | Moderate (25–30%) |
| Progression to ESRD | Delayed | Slower |
| Use with Diabetes | Safe | Safe |
| Edema Risk | Slightly higher | Low |
Combining Vanrafia with RAAS blockade provides synergistic renal protection.
Patient Counseling Tips :
- Take the tablet daily at the same time.
- Monitor weight daily for signs of fluid retention.
- Report shortness of breath or swelling immediately.
- Avoid pregnancy – use contraception.
- Don’t abruptly stop the drug without physician advice.
Conclusion :
Vanrafia is a revolutionary advance in nephrology, especially for patients with persistent proteinuria despite standard treatment. By targeting the endothelin pathway, it acts on a key factor in kidney damage and offers hope to millions of people struggling with chronic kidney disease. Its approval in 2025 marks a new chapter in personalized kidney care.
As with all medicines, regular follow-up and monitoring are necessary to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) :
Q1. What is Vanrafia used for?
Q2. How does Vanrafia help the kidneys?
Q3. Is Vanrafia a cure for kidney disease?
Q4. Can Vanrafia be taken with ACE inhibitors?
Q5. What are the side effects?
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any medical decisions.

