Table of Contents
Introduction :
Lung cancer is one of the most challenging cancers to treat, especially in its advanced stages. As scientists and pharmaceutical companies strive for better results, one promising treatment that has garnered attention in recent years is telisotuzumab adizutecan. This antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is making waves in clinical trials for a targeted approach to cancer treatment.
What is Telisotuzumab Adizutecan?
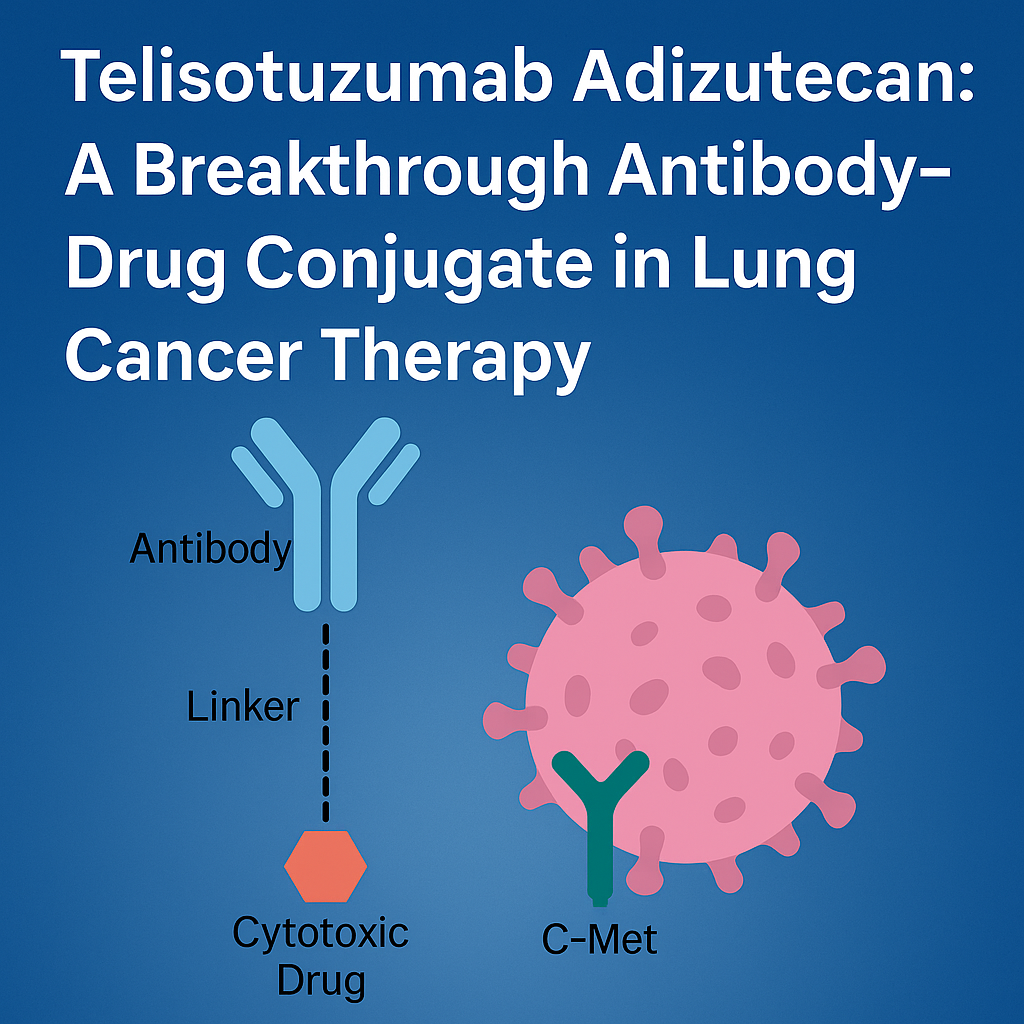
- Telisotuzumab Adizutecan, abbreviated as Teliso-V, is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) developed by AbbVie. It is designed to target c-Met overexpressing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), specifically in patients without the MET exon 14 skipping mutation.
- It combines a monoclonal antibody (telisotuzumab) that targets the c-Met receptor with a cytotoxic drug payload (topoisomerase I inhibitor – deructecan). This fusion allows for precise targeting of cancer cells, sparing healthy tissue, and minimizing systemic toxicity.
What is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) ?
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for about 85% of all lung cancer cases. It develops in the tissues of the lungs, typically in the cells lining the air passages.
🔬 Types of NSCLC –
NSCLC includes several subtypes, which are classified based on the kind of cells found in the tumor:
1.Adenocarcinoma
- Most common subtype of NSCLC
- Starts in mucus-producing glandular cells
- Often found in non-smokers or former light smokers
- Typically located in the outer parts of the lungs
2.Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Begins in the flat cells lining the inside of the airways
- Strongly linked to smoking
- Often found in the central part of the lungs
3.Large Cell Carcinoma
- A less common, aggressive type
- Can appear in any part of the lung
- Grows and spreads quickly
Mechanism of Action (MOA):
The mechanism of action of telisotuzumab adizutecan is what makes it so innovative:
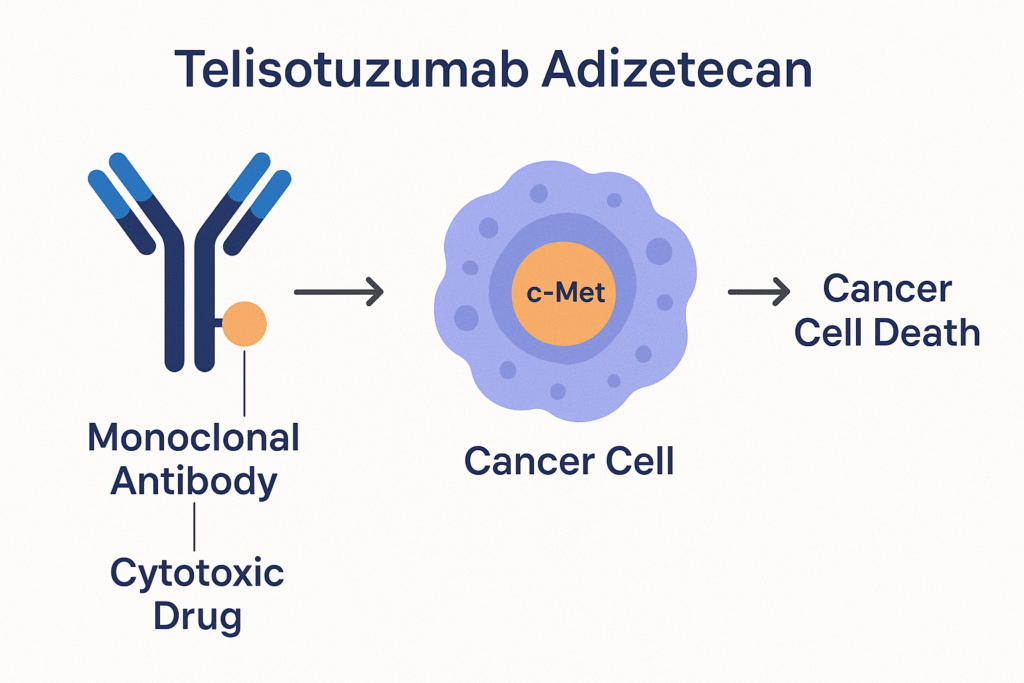
• The telisotuzumab antibody specifically binds to c-Met, a receptor tyrosine kinase that is overexpressed in many tumors, including NSCLC.
• After binding, the drug-antibody complex is internalized into the cancer cell.
• Once inside, the derxutecan payload is released, which inhibits topoisomerase I, which prevents DNA replication, ultimately leading to cancer cell death.
This dual mechanism ensures selective cytotoxicity in c-Met-positive cells while minimizing damage to normal tissue.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy :
Telisotuzumab Adizutecan has shown promising results in clinical trials:
LUMINOSITY Trial (Phase II)
- Population: Patients with advanced/metastatic NSCLC and c-Met overexpression.
- Findings:
- Overall Response Rate (ORR): Approximately 52% in high c-Met expressing tumors.
- Disease Control Rate (DCR): Over 70%.
- Median Progression-Free Survival (PFS): Around 5.5 months.
Key Insights:
- More effective in EGFR wild-type patients.
- Patients with prior TKI treatment responded well.
Mild to moderate adverse effects, with manageable toxicity profile.
Indications and Uses :
Although not yet FDA-approved (due mid-2025), Telisotuzumab Adizutecan is being investigated for:
• Advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with high c-Met expression
• Second-line therapy after failure of EGFR inhibitors or chemotherapy
• Potential use in other solid tumors expressing c-Met (exploratory study)
Dosage and Administration:
Note: Dosage may vary depending on trial protocol.
- Standard Dose (Clinical Trials):
1.9 mg/kg administered intravenously every 3 weeks. - Administration Time:
Infusion over 30–90 minutes under the supervision of a trained oncologist. - Monitoring Required:
- Liver function tests (LFTs)
- Complete blood counts
- Imaging for tumor response
Side Effects and Safety Profile :
Most patients tolerate Telisotuzumab Adizutecan well. However, like most ADCs, it carries potential side effects:
| Common Side Effects | Severity |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Mild to Moderate |
| Fatigue | Moderate |
| Diarrhea | Mild |
| Decreased appetite | Mild |
| Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) | Severe but rare |
| Anemia and Neutropenia | Moderate |
Note: Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) is a serious potential complication and requires immediate medical attention if respiratory symptoms occur.
Precautions and Warnings:
- Avoid during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Monitor for ILD and pulmonary symptoms
- Use with caution in patients with:
- Pre-existing lung conditions
- Liver or kidney impairment
- Avoid live vaccines during treatment
Current Status and Future Outlook
As of 2025, telisotuzumab adizutecan is not yet FDA approved, but has received Fast Track designation from the FDA for NSCLC.
Upcoming Developments:
- Phase III trials are currently underway to confirm efficacy in a larger population.
- Combination therapy with checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab or pembrolizumab is under ongoing research.
- Potential for expanded indications in gastric, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers that show MET overexpression.
Conclusion:
Telisotuzumab adizutecan represents a new era in targeted cancer therapy. With its precise mechanism of action, promising clinical results, and manageable side effects, it is poised to become a key player in the fight against non-small cell lung cancer.
While still under investigation, its future looks promising. Patients with high c-Met expression could soon benefit from a more personalized, effective, and safe treatment option.
FAQs about Telisotuzumab Adizutecan:
Question 1. Is telisotuzumab adizutecan approved by the FDA?
Question 2: What cancers can telisotuzumab adizutecan treat?
Question 3: How is telisotuzumab adizutecan different from other lung cancer treatments?
Question 4: What are the major side effects?
Question 5: Who is eligible for telisotuzumab adizutecan?
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any medical decisions.